- After Completion of this Course, Students will get complete knowledge of hydraulics, based on syllabus of IoE and will be able to secure good score in IoE exam.
- Students are required to have knowledge of Hydraulics, based on syllabus of IoE
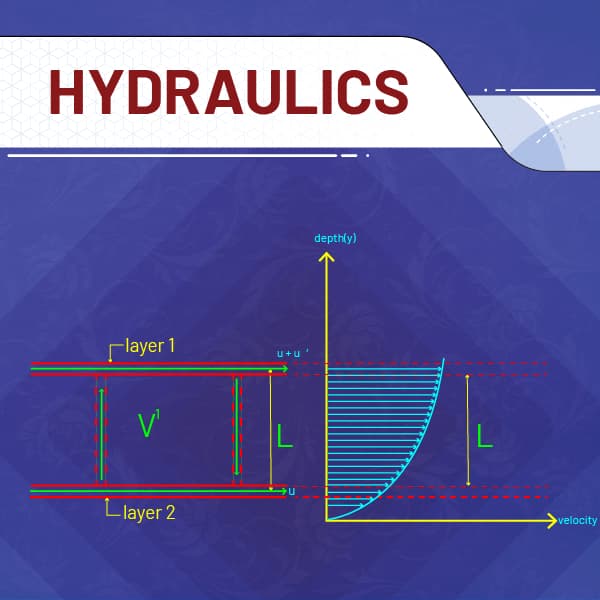
The videos herein are strictly based on syllabus of Institute of Engineering Tribhuvan University, Nepal promoting "e-Learning in Nepal" and are made with intention to provide guidance to the "Bachelor in Engineering(BE) appearing students", for securing good results. The course tries to cover all the basics of Hydraulics. This course also comprises also have the solution of most frequently asked questions in final exam of BE with numerical. We strongly believe that, viewers will be benefited from these videos and the thirst of curiosity of viewers will be quenched! Feedbacks and suggestion to improve are always welcome and highly appreciated!