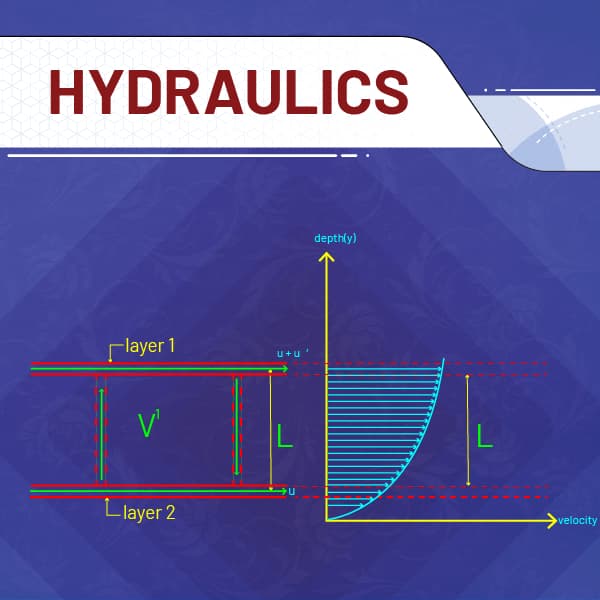
- After Completion of this Course, Students will get complete knowledge of hydraulics, based on syllabus of IoE and will be able to secure good score in IoE exam.
- 1. Syllabus and Marks distribution.mp4 00:05:23
- 1. Pipe flow (differences between pipe flow and open channel flow).mp4 00:13:16
- 2. Reynold's experiment and flow based on Reynold's number.mp4 00:08:48
- 3. Laminar flow in circular pipe (expression for shear stress).mp4 00:14:48
- 4. Laminar flow in circular pipe (velocity distribution).mp4 00:08:56
- 5. Relation between average velocity and maximum velocity.mp4 00:09:10
- 6. Laminar flow in circular pipe (head loss).mp4 00:07:35
- 7. Numerical 1 (laminar flow).mp4 00:24:04
- 8. Numerical 2 (laminar flow).mp4 00:19:41
- 9. K.E. and momentum correction factors.mp4 00:07:27
- 10. Calculation of K.E. and momentum correction factors for laminar flow.mp4 00:10:36
- 11. Turbulent flow (basic features).mp4 00:09:32
- 12. Shear stress development in turbulent flow.mp4 00:05:44
- 13. Boussinesq theory of turbulence.mp4 00:04:38
- 14. Reynold's principle of turbulence.mp4 00:05:37
- 15. Prandtl's mixing length theory.mp4 00:08:37
- 16. Velocity distribution for turbulent flow (Prandtl's universal velocity distribution, applicable for both smooth and rough pipe).mp4 00:12:53
- 17. Analysis of velocity distribution in turbulent flow.mp4 00:08:27
- 18. Hydrodynamically smooth and rough pipe.mp4 00:07:18
- 19. Velocity distribution equation for turbulent flow in smooth pipe.mp4 00:13:09
- 20. Velocity distribution equation for turbulent flow inrough pipe.mp4 00:04:47
- 21. Velocity distribution equation in terms of mean velocity.mp4 00:09:13
- 22. Relation between velocity at any point and average velocity, location of average velocity.mp4 00:08:51
- 23. Darcy-Weisbach equation.mp4 00:17:15
- 24. Resistance to flow of fluid in smooth and rough pipes.mp4 00:24:15
- 25. Numerical 1 (Turbulent flow).mp4 00:16:05
- 26. Numerical 2 (Turbulent flow).mp4 00:10:06
- 27. Numerical 3 (Turbulent flow).mp4 00:10:33
- 28. Numerical 4 (Turbulent flow, concept of hydraulic radius).mp4 00:15:30
- 29. Numerical 5 (Turbulent flow).mp4 00:13:55
- 30. Energy losses in pipe.mp4 00:05:56
- 31. Loss of head due to sudden enlargement of pipe.mp4 00:08:24
- 32. Head loss due to sudden contraction of pipe.mp4 00:07:37
- 33. Other types of minor losses.mp4 00:05:29
- 34. HGL and TEL.mp4 00:09:58
- 35. Numerical (minor losses).mp4 00:11:55
- 36. Numerical (HGL and TEL).mp4 00:25:15
- 1. Three categories of pipe flow problems.mp4 00:07:07
- 2. Category 1 (procedure to solve).mp4 00:03:32
- 3. Numerical (Category 1).mp4 00:06:39
- 4. Category 2 (procedure for solving).mp4 00:05:09
- 5. Numerical 2 (Category 2).mp4 00:11:07
- 6. Numerical 4 (Category 2).mp4 00:08:01
- 7. Category 3 (procedure for solving).mp4 00:04:27
- 8. Numerical 4 (Category 3).mp4 00:10:27
- 9. Numerical 5 (Category 3).mp4 00:09:28
- 10. Pipes in series and parallel, Concept of equivalent pipe, Dupuit's equation.mp4 00:14:52
- 11. Numerical 6 (Pipes in series and parallel).mp4 00:07:58
- 12. Numerical 7 (Pipes in series and parallel).mp4 00:10:37
- 13. Numerical 8 (Pipes in series and parallel).mp4 00:10:16
- 14. Numerical 9 (Pipes in series and parallel, 2075 Baiisakh).mp4 00:13:09
- 15. Siphon and its application (intro).mp4 00:08:01
- 16. Characteristic parameters of siphon.mp4 00:15:54
- 17. Numerical 10 (siphon).mp4 00:08:03
- 18. Numerical 11 (siphon).mp4 00:08:01
- 1. Introduction.mp4 00:12:23
- 2. Procedure for solving Type 1- Problem (3 reservoir problem).mp4 00:08:10
- 3. Numerical (Type 1).mp4 00:10:59
- 4. Procedure for solving Type 2-Problem (3 reservoir problem).mp4 00:08:51
- 5. Numerical 2 (Type 2).mp4 00:16:40
- 6. Procedure for solving Type 3-Problem (3 reservoir problem).mp4 00:11:29
- 7. Numerical 3 (Type 3).mp4 00:27:29
- 8. Numerical 4 (3 reservoir problem. 2073 Magh).mp4 00:15:50
- 9. Numerical 5 (3 reservoir problem, 2073 Bhadra, 2076 Baisakh).mp4 00:16:59
- 10. Introduction to pipe network problem.mp4 00:09:47
- 11. Hardy Cross Method.mp4 00:13:12
- 12. Numerical 6 (Pipe network problem).mp4 00:19:57
- 13. Numerical 7 (Pipe network problem).mp4 00:32:42
- 14. Numerical 8 (Pipe network problem, 2071 Bhadra).mp4 00:14:30
- 15 Numerical 9 (Pipe network problem, 2072 Magh).mp4 00:25:04
- 1. Introduction_1.mp4 00:06:18
- 2. Equation of motion (unsteady flow).mp4 00:15:39
- 3. Analysis of Euler's equation.mp4 00:14:54
- 4. Numerical 1 (Analysis of Euler's equation).mp4 00:15:53
- 5. Numerical 2 (Analysis of Euler's equation).mp4 00:18:17
- 6. Numerical 3 (Analysis of Euler's equation).mp4 00:10:10
- 7. Numerical 4 (Analysis of Euler's equation).mp4 00:08:18
- 8. Continuity equation (unsteady flow).mp4 00:11:21
- 9. Water hammer and its effects.mp4 00:13:17
- 10. Evolution of hydraulic transient waves.mp4 00:13:26
- 11. Time history of water hammer pressure wave.mp4 00:10:08
- 12. Pressure rise due to gradual closure of valve.mp4 00:07:10
- 13. Pressure rise due to sudden closure of valve (rigid pipes).mp4 00:06:04
- 14. Pressure rise due to sudden closure of valve (elastic pipes).mp4 00:11:35
- 15. Numerical 5 (Pressure rise due to evolution of hydraulic transient waves).mp4 00:08:04
- 16. Numerical 6 (Pressure rise due to evolution of transient waves).mp4 00:09:14
- 17. Numerical 7 (Pressure rise due to evolution of transient waves).mp4 00:25:32
- 18. Numerical 8 (Time history of water hammer pressure wave).mp4 00:21:37
- 19. Relief devices against action of water hammer (surge tank).mp4 00:08:39
- 1. Introduction.mp4 00:11:13
- 2. Types of Open Channel.mp4 00:08:22
- 3. Geometric properties of channel section.mp4 00:08:08
- 4. Classification of open channel flow.mp4 00:09:41
- 5. Exam questions.mp4 00:05:25
- 1. Condition for uniform flow.mp4 00:06:50
- 2. Expression for shear stress acting on the channel boundary.mp4 00:07:14
- 3. Uniform flow formula.mp4 00:05:26
- 4. Factors affecting Manning's n.mp4 00:07:34
- 5. Velocity Distribution.mp4 00:12:00
- 6. Some terms in uniform flow computation.mp4 00:13:04
- 7. Solution of uniform flow problems.mp4 00:06:53
- 8. Numerical 1 (Uniform flow).mp4 00:16:14
- 9. Numerical 2 (Uniform flow).mp4 00:04:41
- 10. Numerical 3 (Uniform flow).mp4 00:08:36
- 11. Most efficient channel section condition.mp4 00:03:57
- 12. Most efficient rectangular channel.mp4 00:05:11
- 13. Numerical 4 (most economic rectangular channel).mp4 00:09:39
- 14. Most efficient triangular channel.mp4 00:07:05
- 15. Numerical 5 (most economic triangular channel).mp4 00:05:55
- 16. Most efficient trapezoidal channel.mp4 00:16:06
- 17. Numerical 6 (most economic trapezoidal channel).mp4 00:08:44
- 18. Numerical 6 (most efficient trapezoidal section).mp4 00:08:43
- 19. Numerical 7 (Trapezoidal section, 2073 Bhadra).mp4 00:08:38
- 20. Most efficient circular channel (condition for maximum velocity).mp4 00:15:10
- 21. Most efficient circular channel section (condition for maximum discharge).mp4 00:12:30
- 22. Numerical 8 (most economic circular channel section).mp4 00:08:43
- 23. Numerical 7 (Circular channel section, 2074 Bhadra).mp4 00:10:18
- 28. Conjugate depths and relation between them, related question.mp4 00:08:34
- 1. Specific energy.mp4 00:09:15
- 2. Specific energy curve, condition for critical flow.mp4 00:13:46
- 3. Specific energy, critical depth for rectangular channel.mp4 00:07:04
- 4. Numerical 1 (rectangular channel).mp4 00:10:36
- 5. Numerical 2 (rectangular channel).mp4 00:05:11
- 6. Numerical 3 (rectangular channel).mp4 00:08:53
- 7. Numerical 4 (rectangular channel, 2068 Magh).mp4 00:04:39
- 8. Specific energy, critical depth for triangular channel.mp4 00:06:20
- 9. Numerical 5 (triangular channel).mp4 00:07:24
- 10. Specific energy, critical depth for trapezoidal channel.mp4 00:06:54
- 11. Numerical 6 (Trapezoidal channel).mp4 00:12:02
- 12. Numerical 7 (Trapezoidal channel).mp4 00:09:10
- 13. Discharge-depth curve for a given specific energy.mp4 00:07:35
- 14. Maximum discharge for a rectangular channel section.mp4 00:06:33
- 15. Critical flow and its computation.mp4 00:09:14
- 16. Section factor and Hydraulic exponent during critical flow computation.mp4 00:06:50
- 17. Occurence of critical depth.mp4 00:10:15
- 18. Numerical 8 (Critical flow computation).mp4 00:29:16
- 19. Application of energy principle and critical depth concept.mp4 00:14:40
- 20. Numerical 9 (Provision of hump).mp4 00:14:27
- 21. Numerical 10 (Provision of hump).mp4 00:09:43
- 22. Numerical 11 (2076 Baisakh).mp4 00:15:00
- 23. Numerical 12(Channel with contraction of width).mp4 00:17:22
- 24. Numerical 12 (channel transition, both in cross section and bed slope).mp4 00:12:37
- 25. Numerical 13 (channel transition, 2074 Bhadra).mp4 00:09:04
- 26. Momentum principle in open channel flow.mp4 00:08:27
- 27. Specific force, Specific force curve and condition for critical flow.mp4 00:12:35
- 29. Question based on relation between conjugate depth(2076 Baisakh).mp4 00:06:25
- 1. Introduction.mp4 00:08:35
- 1. Introduction.mp4 00:08:35
- 2. Differential equation for the GVF.mp4 00:10:47
- 2. Differential equation for the GVF.mp4 00:10:47
- 3. Modified forms of GVF equations.mp4 00:10:57
- 3. Modified forms of GVF equations.mp4 00:10:57
- 4. Classification of flow surface profiles.mp4 00:14:02
- 4. Classification of flow surface profiles.mp4 00:14:02
- 5. Characteristics and analysis of flow profiles.mp4 00:09:58
- 5. Characteristics and analysis of flow profiles.mp4 00:09:58
- 6. Mild slope profile (M1, M2 and M3).mp4 00:15:35
- 6. Mild slope profile (M1, M2 and M3).mp4 00:15:35
- 7. Profiles in steep slope (S1, S2 and S3).mp4 00:18:32
- 7. Profiles in steep slope (S1, S2 and S3).mp4 00:18:32
- 8. Profiles in critical slope (C1 and C3).mp4 00:09:21
- 8. Profiles in critical slope (C1 and C3).mp4 00:09:21
- 9. Profiles in horizontal and adverse slopes (H2, H3, A2 and A3).mp4 00:08:07
- 9. Profiles in horizontal and adverse slopes (H2, H3, A2 and A3).mp4 00:08:07
- 10. Analysis of flow profile (break in grades).mp4 00:17:27
- 10. Analysis of flow profile (break in grades).mp4 00:17:27
- 11. Numerical (Analysis of flow in GVF).mp4 00:16:40
- 11. Numerical (Analysis of flow in GVF).mp4 00:16:40
- 12. Direct step method.mp4 00:11:49
- 12. Direct step method.mp4 00:11:49
- 13. Numerical (Direct step method).mp4 00:26:23
- 13. Numerical (Direct step method).mp4 00:26:23
- 14. Numerical (Direct step method).mp4 00:18:02
- 14. Numerical (Direct step method).mp4 00:18:02
- 15. Standard step method.mp4 00:12:01
- 15. Standard step method.mp4 00:12:01
- 16. Numerical (Standard step method).mp4 00:16:34
- 16. Numerical (Standard step method).mp4 00:16:34
- 17. Graphical integration method.mp4 00:06:22
- 17. Graphical integration method.mp4 00:06:22
- 18. Direct integration method.mp4 00:13:30
- 18. Direct integration method.mp4 00:13:30
- 19. Numerical (Direct integration method).mp4 00:19:40
- 19. Numerical (Direct integration method).mp4 00:19:40
- 20. Bresse's method.mp4 00:07:58
- 20. Bresse's method.mp4 00:07:58
- 21. Numerical (Bresse's method).mp4 00:15:27
- 21. Numerical (Bresse's method).mp4 00:15:27
- 1. Introduction.mp4 00:07:37
- 2. Hydraulic jump phenomenon.mp4 00:05:33
- 3. Relationship between sequent depths.mp4 00:14:06
- 4. Energy loss in hydraulic jump.mp4 00:08:38
- 5. Length, height and efficiency of jump.mp4 00:03:43
- 6. Classification of the hydraulic jump.mp4 00:13:21
- 7. Relation between Fr1 and Fr2.mp4 00:05:50
- 8. Numerical 1.mp4 00:15:54
- 9. Numerical 2.mp4 00:11:26
- 10. Numerical 3 (2073 Bhadra).mp4 00:07:51
- 11. Numerical 4.mp4 00:12:35
- 12. Numerical 5.mp4 00:12:33
- 1. Introduction to rigid and mobile boundary channel.mp4 00:05:42
- 2. Design principle of rigid boundary channel (minimum permissible velocity approach).mp4 00:06:30
- 3. Example (Minimum permissible velocity approach).mp4 00:06:49
- 4. Definition of alluvial channel, shear stress distribution on channel boundary, incipient motion condition.mp4 00:07:45
- 5. Design of mobile boundary channel (maximum permissible velocity approach).mp4 00:08:28
- 6. Numerical example (Maximum permissible velocity method).mp4 00:06:55
- 7. Tractive force method (distribution of tractive force).mp4 00:09:57
- 8 Tractive force ratio.mp4 00:12:56
- 9. Shield's tractive force theory.mp4 00:14:16
- 10. Numerical (Shield's tractive force theory).mp4 00:06:05
- 11. Design steps of channel by tractive force method.mp4 00:03:38
- 12. Numerical (Tractive force method).mp4 00:13:00
- 13. Design with regime approach (Kennedy's silt theory and Lindley's regime theory).mp4 00:08:14
- 14. Lacey's regime theory (design steps).mp4 00:06:32
- 15. Numerical (Lacey's regime approach).mp4 00:06:46
- 16. Numerical (2068 Bhadra, similar question in 2076 baisakh).mp4 00:10:55
- 17. Numerical (2068 magh, 2071 magh).mp4 00:06:23
- 18. Formation of river beds based on shear stress.mp4 00:10:41
- 1. Chapter 7 (determination of upstream and downstream depth when there is hump in the downstream).mp4 00:28:44
- 2. Chapter 8 (calculation of normal depth and critical depth in wide rectangular channel).mp4 00:11:46
- 3. Chapter 8 (determination of normal depth in trapezoidal channel).mp4 00:23:11
- 4. Chapter 9 (calculation of sequent depths and energy loss during hydraulic jump).mp4 00:11:49
- 2075 Bhadra|1. Q. No. 1.a.mp4 00:07:14
- 2075 Bhadra|2. Q. No. 1.b.mp4 00:09:53
- 2075 Bhadra|3. Q. No. 2.a.mp4 00:06:44
- 2075 Bhadra|4. Q. No.2.b.mp4 00:28:52
- 2075 Bhadra|5. Q. No. 3.a.mp4 00:15:47
- 2075 Bhadra|6. Q. No. 3.b.mp4 00:07:54
- 2075 Bhadra|7. Q. No. 4.a.mp4 00:12:44
- 2075 Bhadra|8. Q. No.4.b.mp4 00:04:12
- 2075 Bhadra|9.1 Q. No. 4.c.mp4 00:10:13
- 2075 Bhadra|10. Q. No. 5.a.mp4 00:06:47
- 2075 Bhadra|11. Q. No. 5.b.mp4 00:08:48
- 2076 Baisakh|1. Q. No. 1.a.mp4 00:17:10
- 2076 Baisakh|2. Q. No. 1.b.mp4 00:13:49
- 2076 Baisakh|3. Q. No. 2.a.mp4 00:14:03
- 2076 Baisakh|4. Q. No. 2.b.mp4 00:10:32
- 2076 Baisakh|5. Q. No. 3.a.mp4 00:08:15
- 2076 Baisakh|6. Q. No. 3.b.mp4 00:05:12
- 2076 Baisakh|7. Q. No. 3.c.mp4 00:17:59
- 2076 Baisakh|8. Q. No. 4.a.mp4 00:09:51
- 2076 Baisakh|9. Q. No. 4.b.mp4 00:13:42
- 2076 Baisakh|10. Q. No. 5.a.mp4 00:10:56
- 2076 Baisakh|11. Q. No. 5.b.mp4 00:14:26
- 2076 Bhadra|1. Q. No. 1.a.mp4 00:15:08
- 2076 Bhadra|2. Q. No. 1.b.mp4 00:09:37
- 2076 Bhadra|3. Q. No. 1.c.mp4 00:09:05
- 2076 Bhadra|4. Q. No. 2.a.mp4 00:28:40
- 2076 Bhadra|5. Q. No. 2.b.mp4 00:10:09
- 2076 Bhadra|6. Q. No. 3.a.mp4 00:05:32
- 2076 Bhadra|7. Q. No. 3.b.mp4 00:05:09
- 2076 Bhadra|8. Q. No. 3.c.mp4 00:08:29
- 2076 Bhadra|9. Q. No. 4.a.mp4 00:05:54
- 2076 Bhadra|10. Q. No. 4.b.mp4 00:09:05
- 2076 Bhadra|11. Q. No. 4.c.mp4 00:03:36
- 2076 Bhadra|12. Q, No. 5.a.mp4 00:14:37
- 2076 Bhadra|13. Q. No. 5.b.mp4 00:09:39
- 2077 Poush|1. Q. No. 1.a.mp4 00:24:11
- 2077 Poush|2. Q. No. 1.b.mp4 00:11:28
- 2077 Poush|3. Q. No. 2.a.mp4 00:14:51
- 2077 Poush|4. Q. No. 2.b.mp4 00:07:56
- 2077 Poush|5. Q. No. 3.a.mp4 00:12:03
- 2077 Poush|6. Q. No. 3.b.mp4 00:03:50
- 2077 Poush|7. Q. No. 3.c.mp4 00:11:07
- 2077 Poush|8. Q. No. 4.a.mp4 00:13:48
- 2077 Poush|9. Q. No. 4.b.mp4 00:12:54
- 2077 Poush|10. Q. No. 5.a.mp4 00:13:50
- 2077 Poush|11. Q. No. 5.b.mp4 00:10:17
- 2078 Baisakh|1. Q. No. 1.a.mp4 00:14:55
- 2078 Baisakh|2. Q. No. 1.b.mp4 00:06:03
- 2078 Baisakh|3. Q. No. 2.a.mp4 00:13:08
- 2078 Baisakh|4. Q. No. 2.b.mp4 00:13:05
- 2078 Baisakh|5. Q. No. 3.a.mp4 00:02:53
- 2078 Baisakh|6. Q. No. 3.b.mp4 00:14:51
- 2078 Baisakh|7. Q. No. 3.c.mp4 00:07:54
- 2078 Baisakh|8. Q. No. 4.a.mp4 00:10:22
- 2078 Baisakh|9. Q. No. 4.b.mp4 00:22:17
- 2078 Baisakh|10. Q. No. 5.a.mp4 00:24:58
- 2078 Baisakh|11. Q. No. 5.b.mp4 00:16:10
- Students are required to have knowledge of Hydraulics, based on syllabus of IoE
The videos herein are strictly based on syllabus of Institute of Engineering Tribhuvan University, Nepal promoting "e-Learning in Nepal" and are made with intention to provide guidance to the "Bachelor in Engineering(BE) appearing students", for securing good results. The course tries to cover all the basics of Hydraulics. This course also comprises also have the solution of most frequently asked questions in final exam of BE with numerical. We strongly believe that, viewers will be benefited from these videos and the thirst of curiosity of viewers will be quenched! Feedbacks and suggestion to improve are always welcome and highly appreciated!